Cell Membrane Structure Journal
With the rapid development of nanotechnology and single-molecule techniques our understanding of cell membranes has substantially increased.
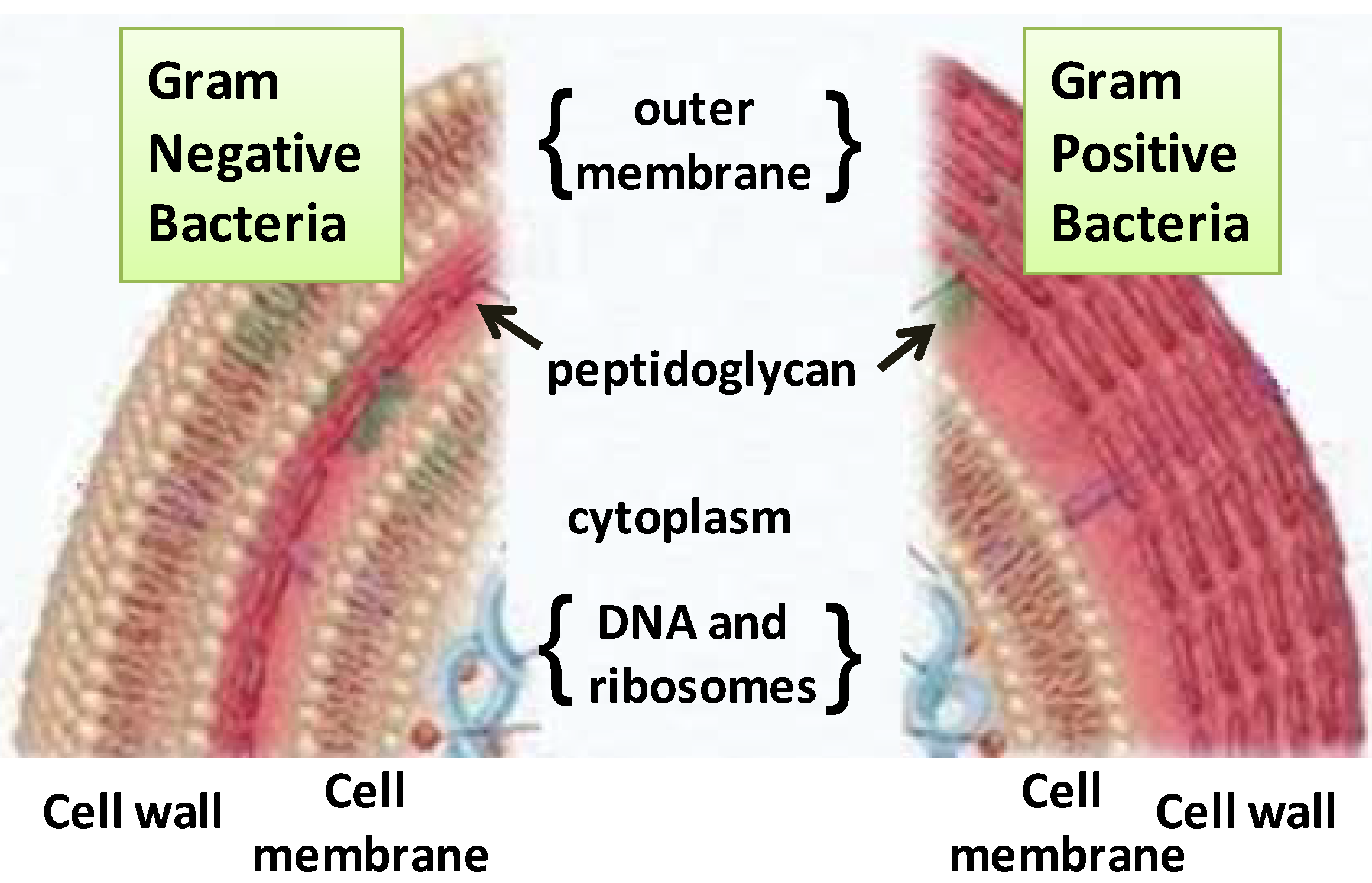
Cell membrane structure journal. THE CELL MEMBRANE 1. The proteins and lipids in membranes form collectives the biology and physics of which will remain a challenge and a source for new insights in years to come. The current views on the structure and function of biological membranes the role of their lipid protein and carbohydrate components in the maintenance of cell vital activity are summarized.
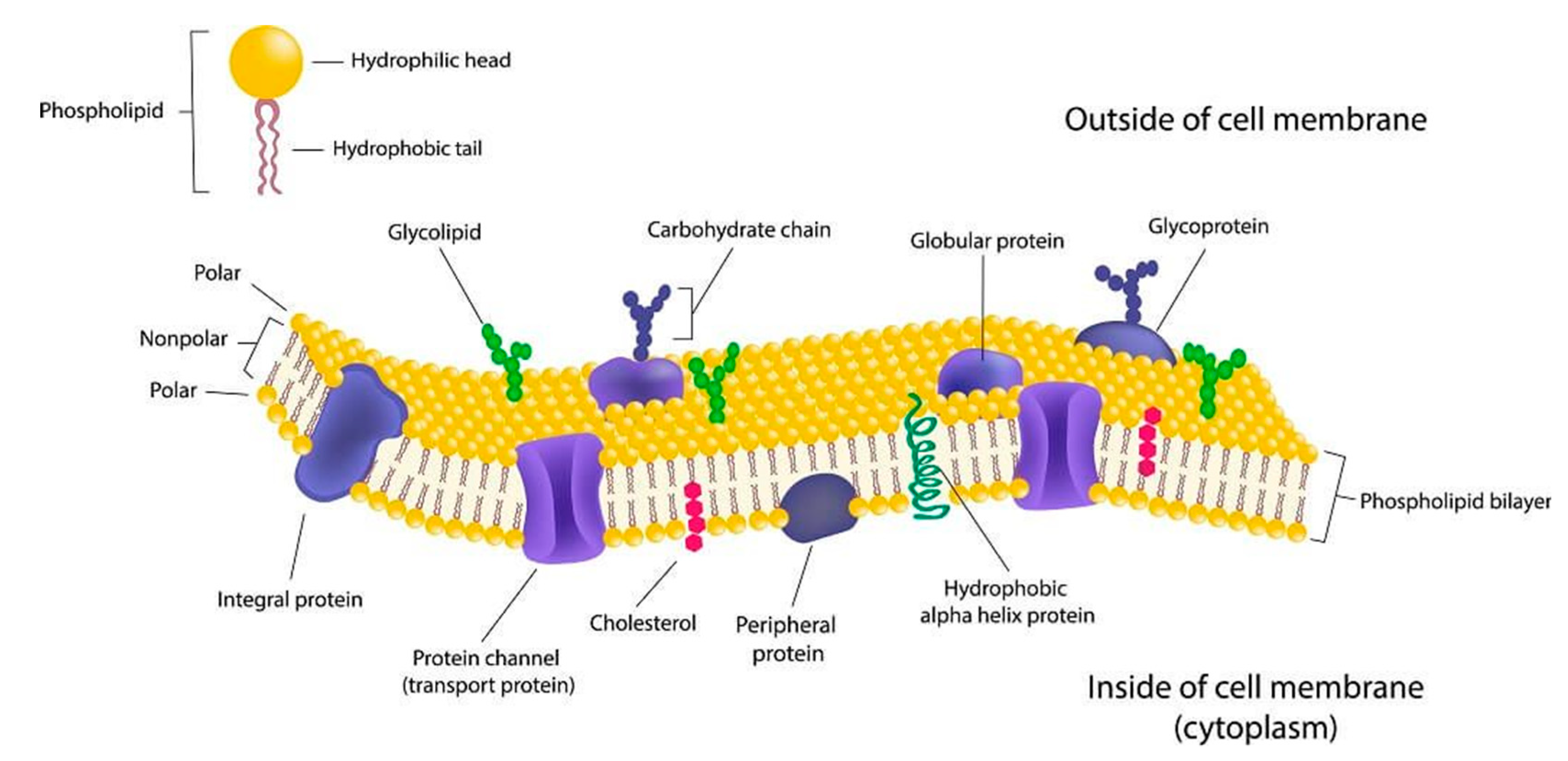
3 cholesterol-enriched domains exist in the cell membrane. The paucimolecular unit membrane model of the structure of the plasma membrane is critically reviewed in relation to current knowledge of the chemical and enzymatic composition of isolated plasma membranes the properties of phospholipids the chemistry of fixation for electron microscopy the conformation of membrane proteins the nature of the lipid-protein bonds in membranes and possible mechanisms of transmembrane transport and membrane. THE formation of single stable bimolecular lipid and proteolipid1 membranes up to 10 mm2 in area has been accomplished routinely in 01 M saline solution by methods analogous to the formation of.
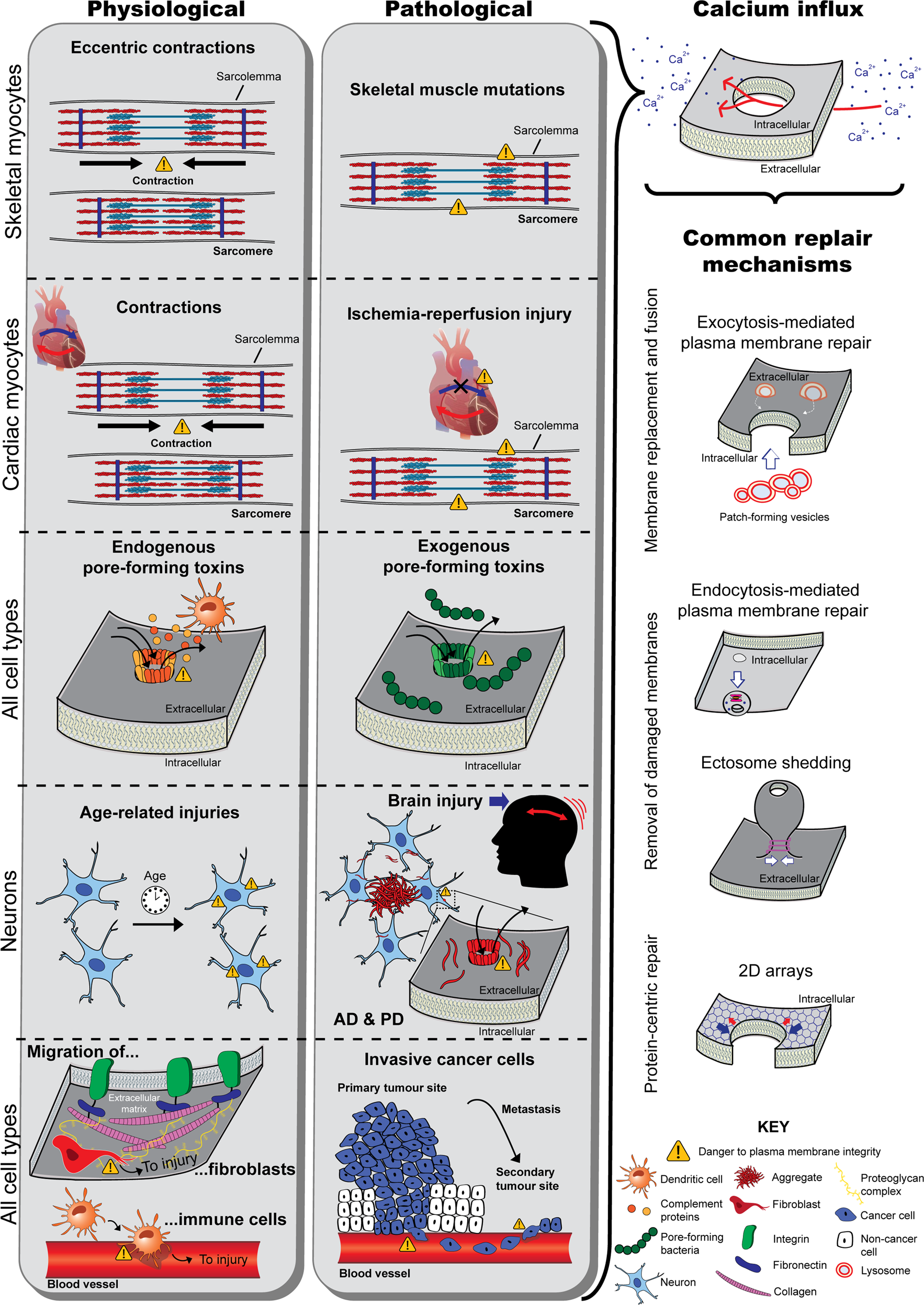
The work described here addresses questions from a broad range of areas including cell adhesion membrane trafficking and activation of cells. The cell membrane is one of the most complicated biological complexes and long-term fierce debates regarding the cell membrane persist because of technical hurdles. Considerable progress has been made in understanding the roles played by two membrane lipids.
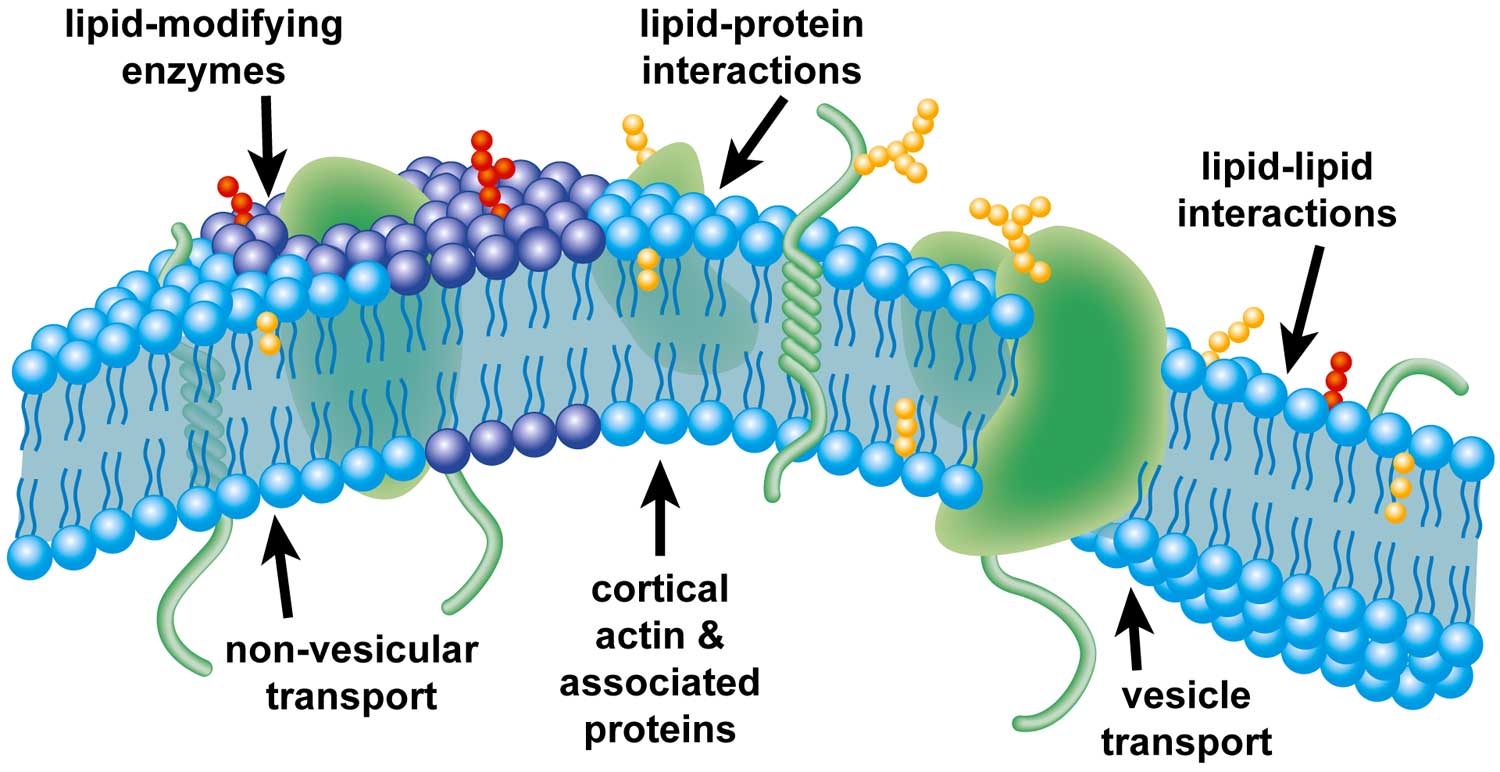
Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes. For the same token a bacterial toxin does not insert into the membrane through a nonlamellar phase nor two membranes fuse via a rhombohedral phase. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out.
1 15 Amer Assoc Blood Banks Arlington VA 1986 Google Scholar. The fascination of membrane research is that the functionality of the cell membrane is dependent on the carefully orchestrated and mutually interdependent properties of lipids and proteins. The Journal of Membrane Biology is dedicated to publishing high-quality science related to membrane biology biochemistry and biophysics.
Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals. Original Research Cell membranes are commonly considered fundamental structures having multiple roles such as confinement storage of lipids sustain and control of membrane proteins. The cell membrane is a complex barrier separating every cell from its external environment.