Cellular Respiration Formula With States

The overall unbalanced chemical equation for cellular respiration is.
Cellular respiration formula with states. There are three main stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and electron transportoxidative phosphorylation. Cellular Respiration Definition.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. In simplified terms it is. Explain why aerobic cellular respiration results in 36 ATPs per glucose in eukaryotic cells and 38 ATPs per glucose in prokaryotic cells.
Cellular Respiration as a Series of Reduction-Oxidation Reactions. There are many ways to compare and contrast these. Someone wrote the balanced equation heres the word equation.
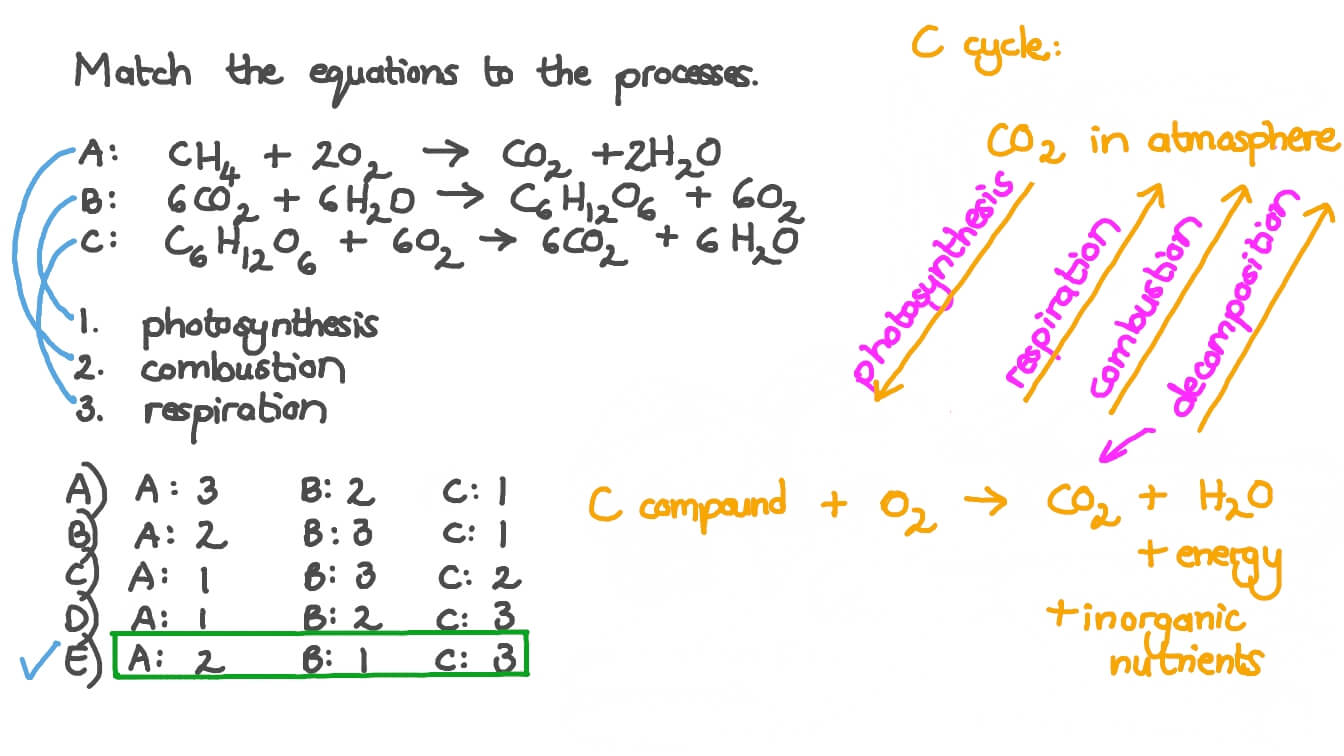
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is C6H1206 6O2 6CO2 6H2O energy ATP. Redox describes all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. Cellular respiration on the other hand the process of using glucose and oxygen to create ATP or cellular energy is almost the opposite of photosynthesis.
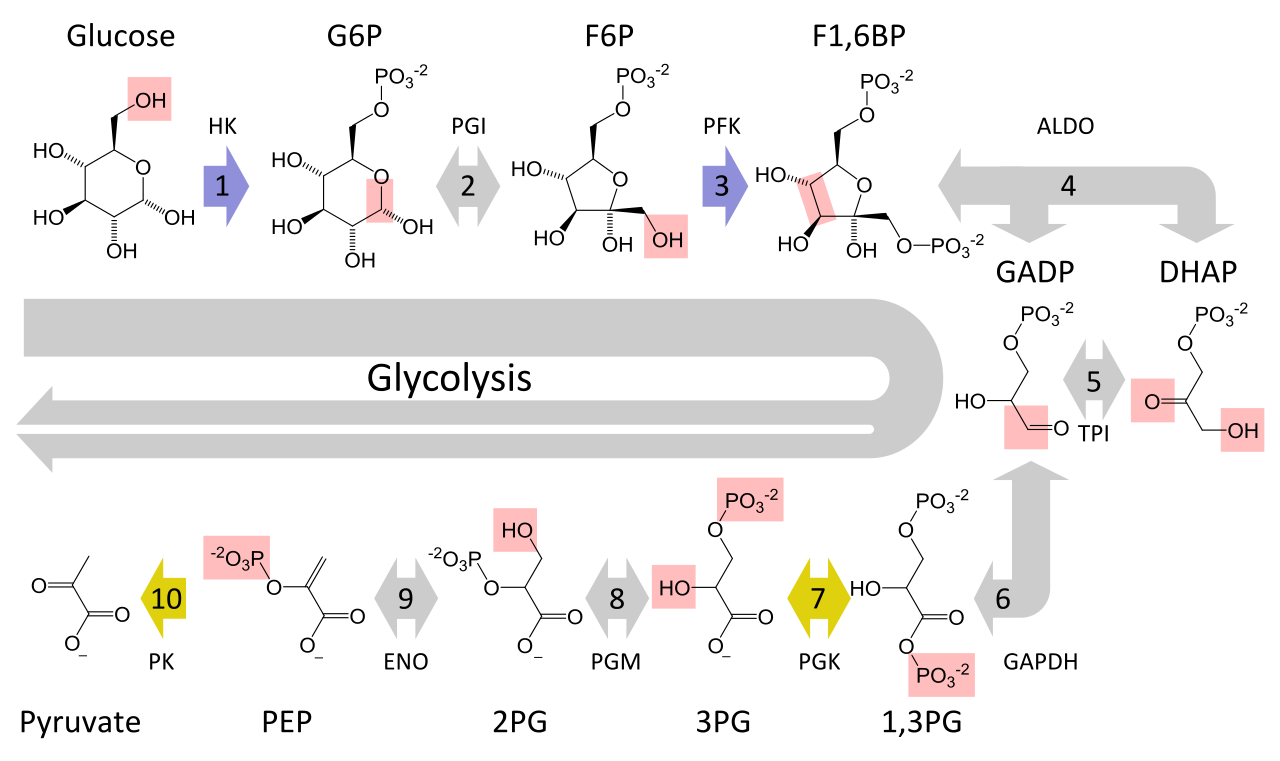
The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as.
State the number of ATPs produced during glycolysis the transition reaction the Krebs cycle and the oxidative-phosphorylation process. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. However cellular or aerobic respiration takes place in stages including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.