Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy.
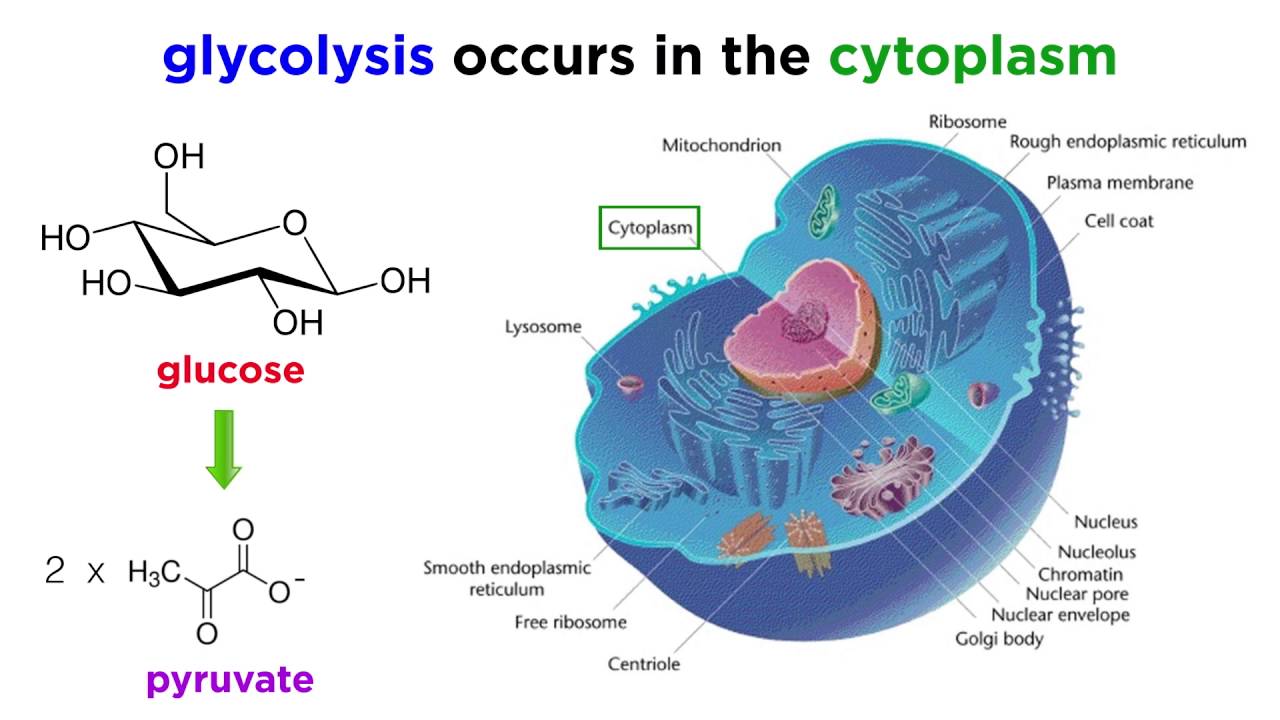
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP.
Cellular respiration biology definition. Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase.
Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.