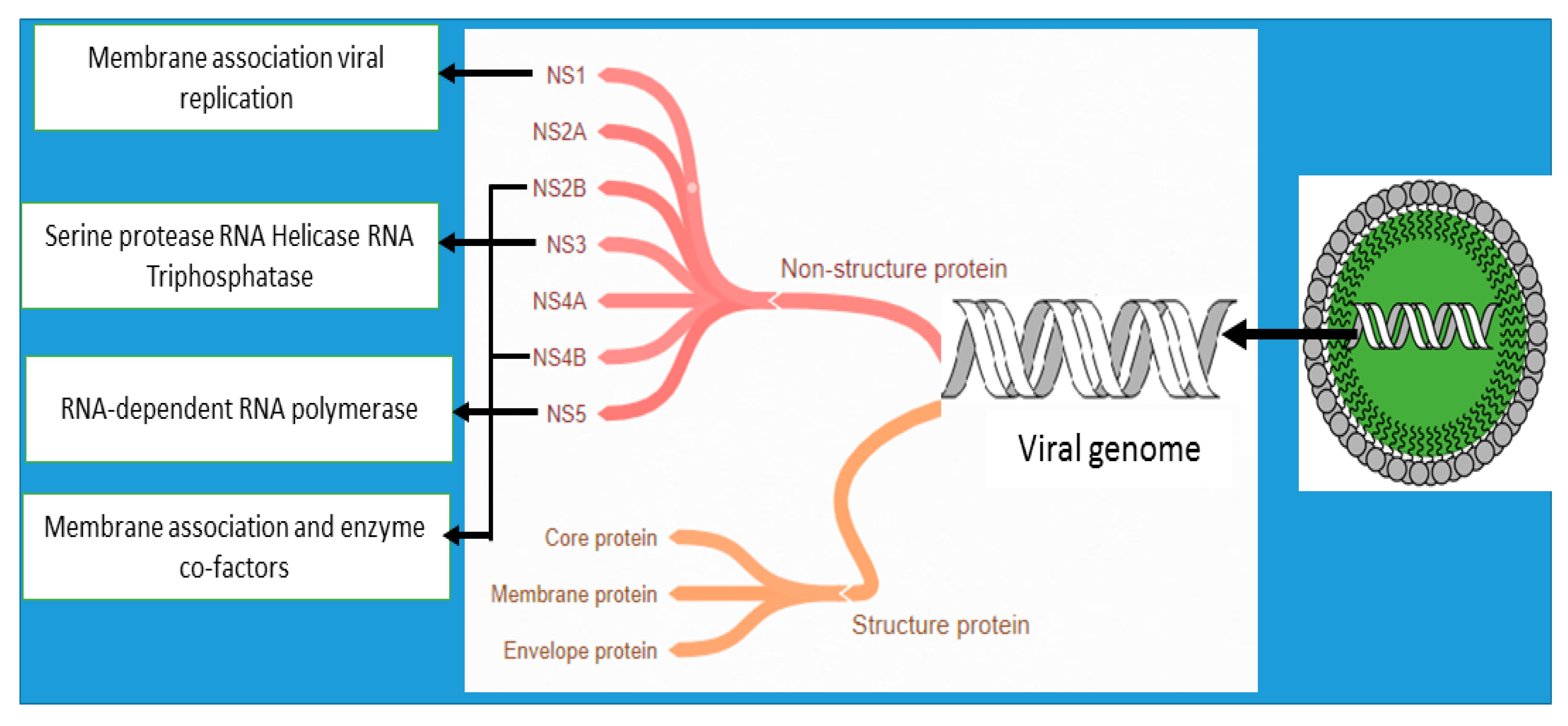
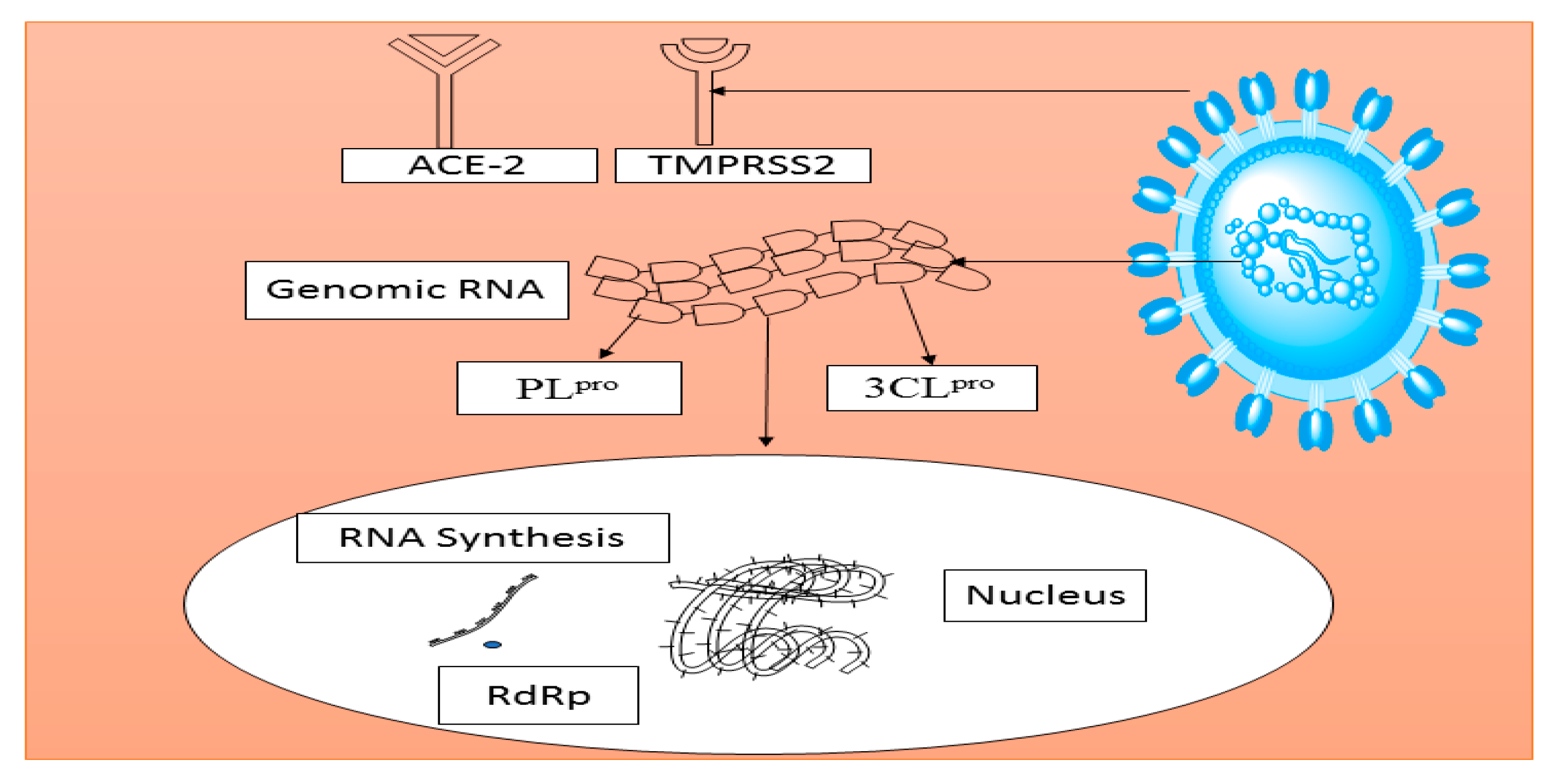
Transgenic Plants And Animals Wikipedia
Plant can be used as bioreactor transgenic plants which can be used to produce the proteins or peptides encoded by the introduced foreign genes in vaccine production against animal and human diseases.
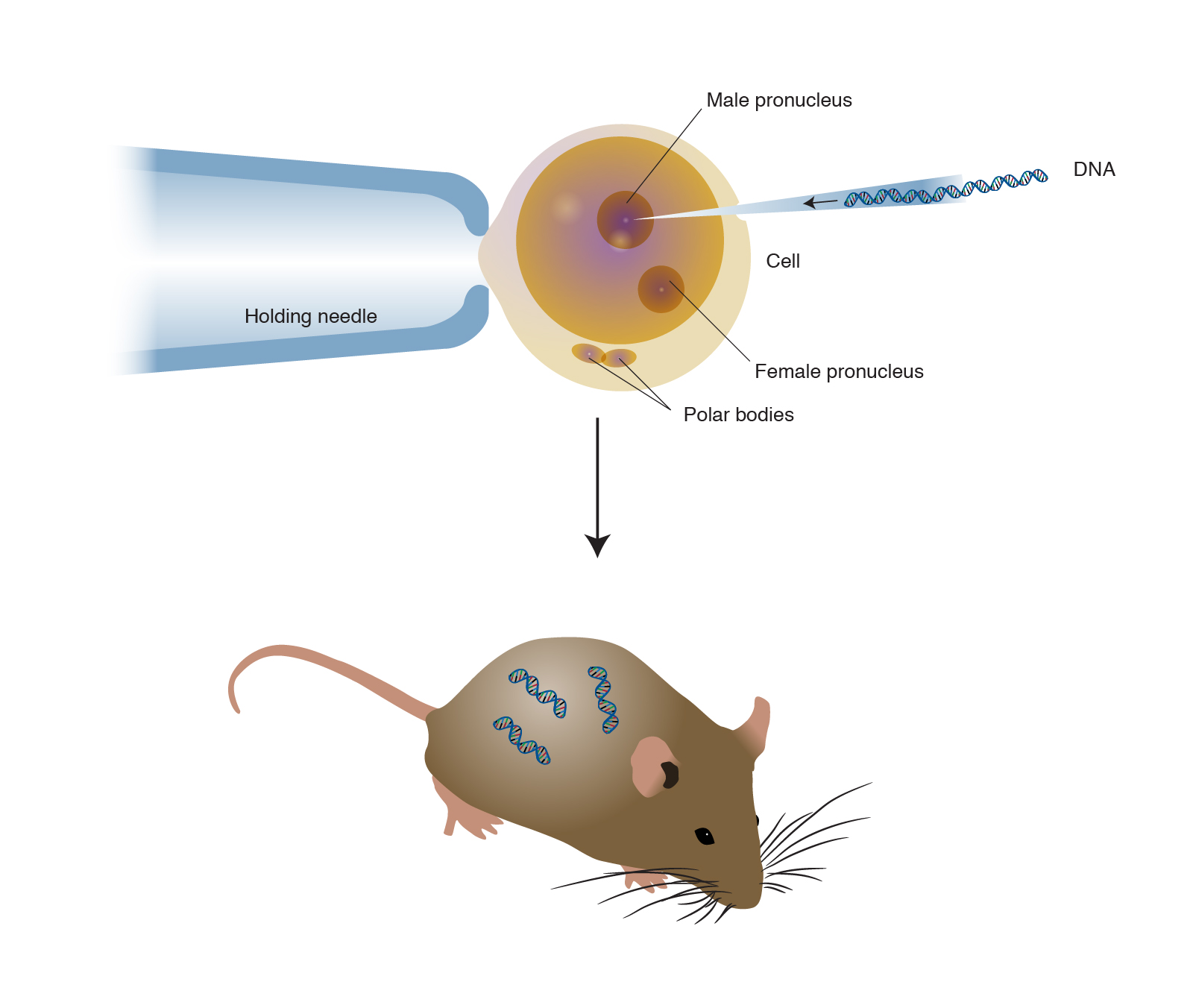
Transgenic plants and animals wikipedia. These genes are passed on to the successive generations. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been inserted into its genome. TRANSGENESIS- The phenomenon of introduction of exogenous DNA into the genome to create and maintain a stable and heritable character.
Transgenic animals for the production of therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are produced by transferring fertilized transgene-carrying embryos to recipient animals. Although several recombinant proteins used in medicine are successfully produced in bacteria some proteins require a eukaryotic animal host for proper processing. The cell uses CO 2 water minerals and sun light to synthesise thousands of valuable and complex products which are the basis of animals life.
I to obtain information on gene function and regulation as well as on human diseases ii to obtain high value products recombinant pharmaceutical proteins and xeno-organs for humans to be used for human. Transgenic Plants as Bioreactor Molecular Farming. Transgenic models are more precise in comparison to traditional animal models for example the oncomouse with its increased susceptibility to tumor development enables results for carcinogenicity studies to be obtained within a shorter time-frame thus reducing the course of tumor development in experimentally affected animals.
Transgenic plants and animals Transgenic plants are plants that have been genetically engineered a breeding approach that uses recombinant DNA techniques to create plants with new characteristics. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. Transgenic plants potato and cotton were for the first time made available to farmers in USA.
The very purpose of production of transgenic plants is for their commercial importance with high productivity. The aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. By the year 1998-99 five major transgenic crops cotton maize soybean canola and potato were in widespread use.
For this reason the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals such as sheep goats chickens and mice. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it to be incorporated into the DNA of the host and to be expressed correctly by the cells of the host. Transgenic plants can produce a variety of proteins used in diagnostics for detecting and curing human and animal diseases in large scale with low cost.